We talk about networking and how we should apply it to a real-world case.
On the first two weeks, we've talked about Network Topology Types and Network Architecture Components, CDs and BDs.
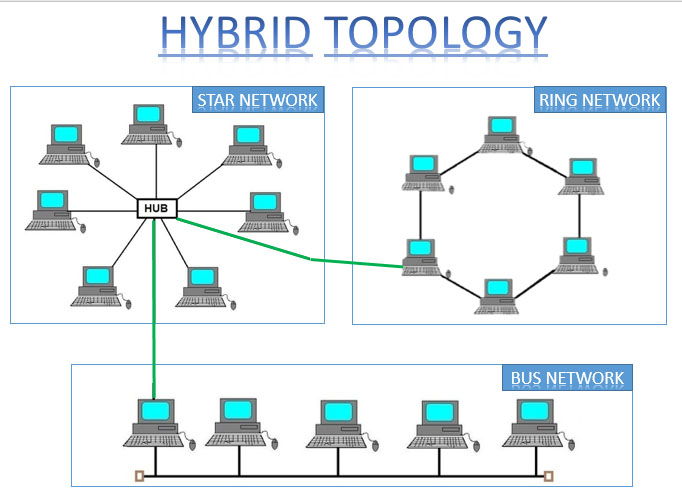
We have talked about five different types of topologies and these are the Bus, Ring, Star, Mesh and Hybrid topologies.
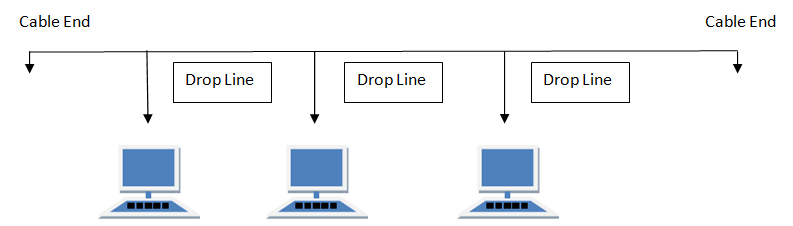
The Bus topology is a network type in which all computers are connected to a single cable;thus, making it simple and cheap but risky because if there's a fault in the bus the whole network will fail.
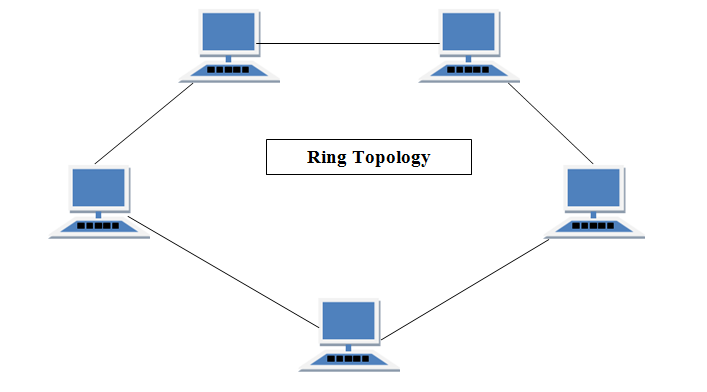
The Ring topology is like (of course) a ring because each computer is connected to another computer, making each device have two neighboring devices making it look like a ring.
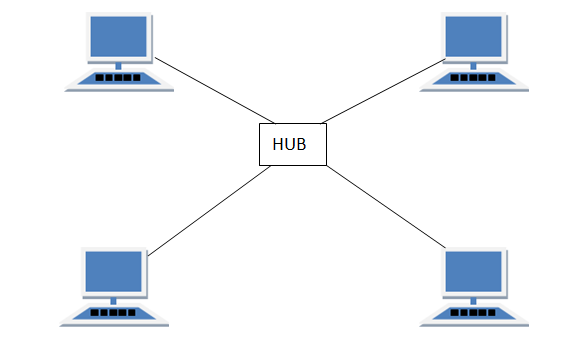
The Star topology lets its devices communicate simultaneously but if the hub or switch fails then the whole network will stop working.
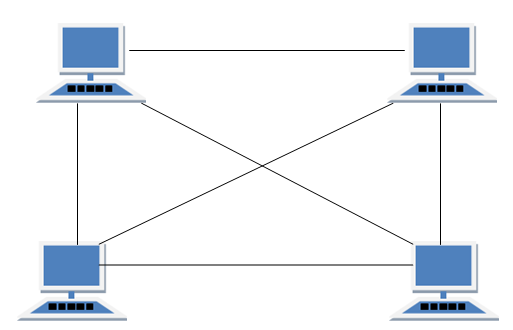
The Mesh topology lets its devices transmit data simultaneously and if one node fails, it will not cause the whole network to fail too but this topology is expensive since a lot of cables and maintenance are needed.
and last but certainly not least, the Hybrid topology. It combines two or more topologies. This is good because it gets all the advantages of both topologies but at the same time, it is somewhat bad because it also obtains all of the disadvantages of the topologies used. It is effective and flexible but expensive and the design is complex.
We have also talked about the Network Architecture Components which are the Fault Tolerance, Scalability Quality of Service(QoS) and Security. Fault tolerance is mainly the availability of the data, it is about having backups, redundancy, ups, generators and raids. Scalability is the ability of the network to support new users and applications without affecting the service of the existing users. QoS answers the question "Who needs the network more?" It prioritizes the users who need it more. Security is protection and safety to incoming and outgoing data.
CD or Collision Domain is simply the capability of the device to communicate data at the same time.
On the other hand, BD or Broadcast Domain is the ability of the device to transfer data to all other devices in a network segment. A network segment is a portion of the network that is different from the rest of the network by a device such as a repeater, hub, bridge,switch or router.
Repeater - This is a HUB that has less ports
Hub - A hub connects multiple devices in a LAN and transfers data blindly.
Bridge - This is a SWITCH that has less ports
Switch - This also connects multiple devices in a LAN but it sees the data that it transfers.
Router - It's a device that sends packets of data to different networks.
This is so far what we have learned for the past two weeks, not going into too much detail about the lessons since I couldn't possibly talk about everything that our professor have discussed (I don't have that good of a memory). I really enjoy learning about networking since this is something new to me but it's kind of hard to differentiate terms and I get confused. Maybe if I get accustomed to this, I'd probably be able to easily understand it more.